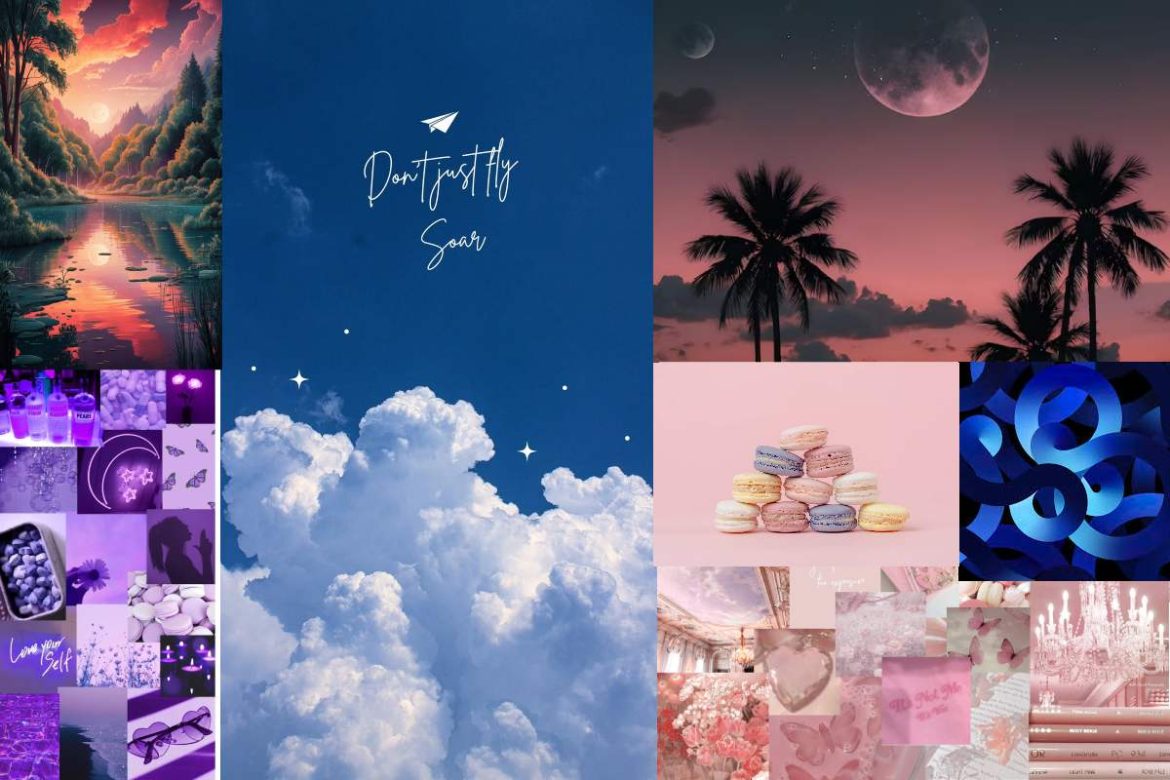
Wallpaper is a thing which can change the mood of a person and have the ability to motivate and can even distract from a situation as its effects lead to drastic change so one should choose their Wallpaper in such a way to get motivated in my view .however Aesthetic Wallpaper refers to visually appealing designs or images used as backgrounds on devices such as computers, phones, or tablets. These wallpapers often evoke certain emotions or styles, improving the overall ambiance and mood of the screen. Aesthetic wallpapers focus on minimalistic, harmonious, and usually artistic visuals
Types of Aesthetic Wallpaper:
- Minimalist Aesthetic:
- Simple
- clean designs with muted colors
- plenty of adverse space,
- frequently featuring geometric shapes or abstract forms
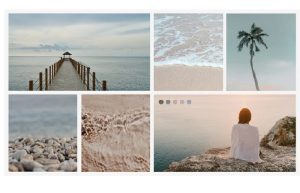

2.Vintage Aesthetic:
- Inspired by past spans,
- featuring grainy textures,
- retro colors,
- nostalgic imagery from the ’60s to the ’90s

3.Nature Aesthetic:
Beautiful landscapes, plants, flowers, and natural elements that promote tranquility and connection with nature.
4.Dark Academia Aesthetic:
- Focuses on scholarly,
- gothic visuals with a dark,
- moody color palette,
- featuring old libraries, candles, and antique items.


5.Pastel Aesthetic:
Soft, light colors like pinks, blues, and yellows, often featuring playful or dreamy elements.

6.Grunge Aesthetic:
Rough, edgy designs with darker tones,
- distressed textures,
- and often rebellious,
- urban imagery.

7.Bohemian Aesthetic:
- Free-spirited designs with earthy tones,
- eclectic patterns, and
- tribal or artistic elements.

Each type reflects a different mood, catering to the personal style and taste of the individual using the wallpaper.
Here is link to download for free Aesthetic wallpaper; https://www.pexels.com/search/aesthetic%20wallpaper/
https://unsplash.com/s/photos/aesthetic
.