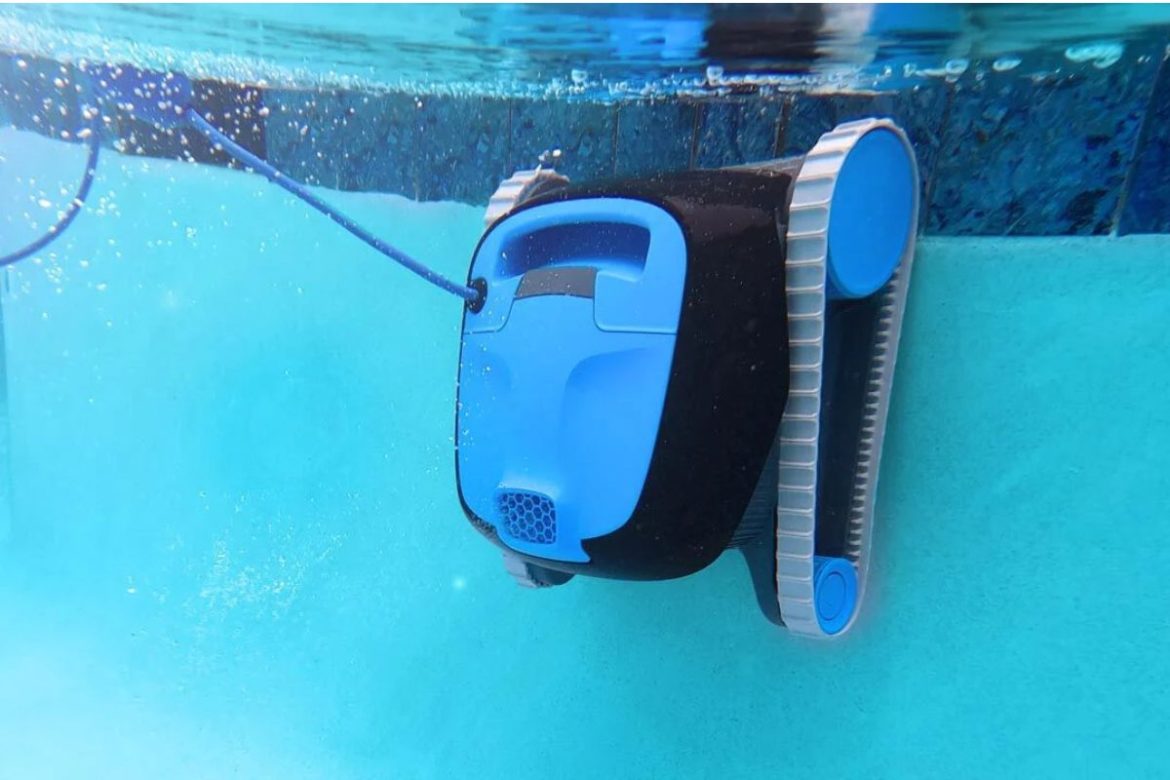
We officially declare Dolphin Nautilus CC as the best in 2023. For many good reasons, it’s easy to understand why.
Let’s start with the actual number of satisfied users. On Amazon, the Nautilus garnered 7,373 reviews. From this stat, 74% gave the product 5 stars, 12% 4 stars, 5% 3 stars, 3% 2 stars, and only 6% were unsatisfied. If these numbers could speak, they would tell us that the Nautilus is a quality machine. Some features that the users love include the easy-to-clean aspect, maneuverability, suction power, and lightweight.
Today, we’ll be taking an in-depth look at this popular pool cleaner to see its features and if it’s the right robot cleaner for you.
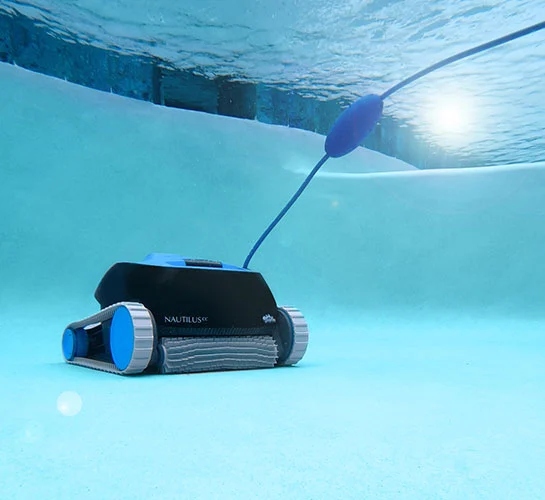

Features of Dolphin Nautilus CC Robotic Pool Cleaner
Swimming pools are a great way to relax, but keeping them clean can be a massive pain. If you have a pool, you have probably tried your hand at cleaning and regretted it. The good thing is that many robotic pool cleaners make cleaning easier. However, not all of them are created equal. We’ll be taking an in-depth look at the Dolphin Nautilus Cc to see if it’s right for you.
In a nutshell, the Dolphin Nautilus CC is one of the most efficient and reliable robotic pool cleaners on the market today. It has all the functionality you’d expect from a high-end pool cleaner but isn’t as expensive as its competitors ($699 at Amazon, $899 for the CC Plus version). This pool cleaner can clean your pool in as little as two hours while continuously scrubbing with its dual-action brushes. It comes with a remote control that can be used to choose between different cleaning modes.
The Nautilus CC by Dolphin is equipped with all the features you need to keep your pool sparkling clean, including a dual-wheel design, dual-bristle brush, and a wash-and-vac cycle for removing more debris. It also has a reinforced cleaner head that lets you easily clean pool walls, corners, and coves. The Nautilus CC Plus also boasts a faster cleaning cycle than previous models, which means that your pool will be sparkling clean to make it safe for swimming.
What You Need to Know About Dolphin Nautilus CC
Cleaning Scheduling
A weekly timer function is a convenient tool that allows you to program your Dolphin Nautilus CC robotic pool cleaner to clean at any hour of the day. If you wish, you can set it to clean once a week, every two weeks, or even once every other month. No matter what you choose, you will have a cleaner pool. You can also set the timer to run the device simultaneously every day if you have to.
Energy Efficient
The average above-ground pool can use up to 1000 gallons of water a year. That’s a lot of wasted water! That’s why it’s great that the Dolphin robotic pool cleaner is energy efficient. It is programmed to clean the pool for up to two hours with just 180 watts. This means up to a whopping 83% power consumption reduction! This is a huge step towards saving energy and money.
CleverClean Navigation
Like the other Dolphin models, the Nautilus CC remain engineered with CleverClean technology. This allows you to clean the inside of your pool faster than traditional methods. The device remain designed with smart navigation patterns. This allows for efficient and thorough cleaning. You can choose from three-speed settings as well.
Easy Filter Removal
The Nautilus CC has an easy-to-clean filter. Just click the filter release button, slip the filter away, wash out any collected debris, and store the device again. The filter unit is accessible at the top of the bot. The filter can trap different sizes of particles, from large to small. Other Dolphin brands like Premier work better if your pool has smaller particles.
What Users Say About Dolphin Nautilus CC
Most pool device review sites hail the Dolphin Nautilus CC as the best mid-range robotic cleaner in 2023.
One aspect of the bot that many users like is its simplicity. People don’t want anything too complicated. It’s nice to have a tool that can help in cleaning your pool environment without making it more of a hassle than it needs to be. The device is simple to use and requires no hoses, additional parts, or chemicals. It’s one of the easiest pool cleaners, even for newbies.
In the user reviews, this product received much praise for its ability to thoroughly clean the pool. A lot of people found it helpful that it could clean all areas of the pool. The filters were large enough to capture all sorts of particles. It remains also mentioned that the tool is powerful enough to move the debris to the filter. Its strong suction capability can remove debris from the water.
They also love that it’s energy efficient. The machine required a lot less electricity than other pool cleaners, which meant they could save money on their power bill. The Dolphin Nautilus CC saves people money because they don’t have to buy special cleaners, which are usually expensive!
The device is easily portable, so people can take it everywhere! It’s the perfect gift for parents and teenagers who love swimming. It is designed to remain lightweight, making it easy for anyone to put it in and take it out of the pool. You can easily lift the machine and drain the excess water. Once outside, you can take out the filter to remove the collected debris.
In terms of negative comments, many people point out that they don’t like that the bot can’t climb stairs. If your pool has stairs, consider this factor before buying this model.
Final Note
Dolphin Nautilus CC is an incredible robotic pool cleaner. It is the best of its kind for many reasons. But the one that really stands out is that it is so easy to use. With other robotic pool cleaners, you have to spend a lot of time with the manual and the different buttons to get the machine started. However, with the Dolphin Nautilus CC, you take it out of the box, place it in the pool, and then it can begin cleaning right away.
The Dolphin Nautilus CC will be the best robotic pool cleaner in 2023. It has an easy-to-clean filter and an efficient scheduling system that cleans your pool better than the rest. It also features a cleaning mode that lets you customize it to your needs. The Nautilus CC can clean your pool in 2 hours, covering the floor, walls, and waterline.